Agriculture: - It is derived from Latin word ‘agricultura’
Agri + Cultura , Agri means ager / field, Cultura means cultivation
That branch of science in which we study about growth of plants and animals for human use is called agriculture.
Agriculture includes-
Que. Why do we have to eat food and how can we provide food to a large number of people in our country?
Ans- Food provide energy to living organisms and this energy is utilized by the organisms for carrying out their various body function. So we have to eat food. In order to provide food for a large population, food has to be produced on a large scale, for this, regular production, proper management and distribution is necessary.
Field: - The land where plants are cultivated is called field.
Crops: - Plants of same kind grown in large quantities in field are called crop plants or crops.
|
Type of Crop |
Examples |
|
Cereals and grain crops |
Maize, Rice, Wheat, Barley, Millet, Paddy |
|
Fibre crops |
Jute, cotton |
|
Pulses (dal or legumes) crops |
Gram, pea, beans, arahar, moong |
|
Oil seeds crops |
Mustard, ground nut, sunflower, soya bean |
|
Root crops |
Sweet Potato, carrot |
|
Tuber crops |
Potato, ginger, tapioca |
|
Sugar crops |
Sugar cane, beetroot |
|
Plantation crops |
Coffee, tea, rubber, coconut |
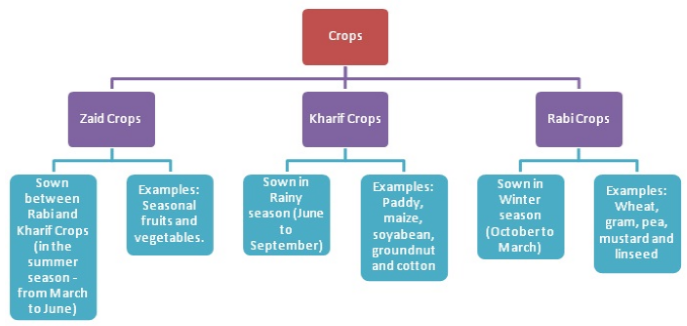
TYPES OF CROPS ( Mainly two)
|
Kharif crops OR Summer crops |
Rabi crops OR Winter crops |
|
|
Kharif crops: - Those crops that are grown during rainy season are called kharif crops.
Ex: - Rice, groundnut, maize, cotton, pulses
* Kharif crops sown between June / July and harvested in September/October.
Rabi crops: - Those crops that are grown during winter season are called rabi crops.
Ex: - Wheat, barley, mustard, potato and peas
* Rabi crops sown between October / November and harvested in March/April.
Horticulture: - Hortus means garden + Culture means cultivation
That branch of science in which we study of plants grown for commercial purpose is called horticulture.
|
Type of Crop |
Examples |
|
Vegetables |
Potato, tomato, cabbage, spinach, onion, radish |
|
Fruits |
Apple, mango, banana, guava, grapes, papaya |
|
Decorative Plants |
Crotons, cactus, bougainvillea, Pam, alcariya |
|
Flowers |
Rose, jasmine, marigold, balsam |
Note:- Zayed Crops:- Those crops that are grown /sown in march /april and harvested before rainy season are called zayed crops.
Ex:- Cucurbits, gourd, bitter gourd(karela), moong.
* Zayed crops do not include any grain crop.
Agricultural practices: - The activities that is done by farmers to cultivation of crops are called agricultural practices.
There are seven types of agricultural Practices (7)
1. Preparation of Soil: To loosen and turn the soil.
2. Sowing: Planting of seeds of a crop in soil.
3. Adding Manure and Fertilisers: Adding essential nutrients to soil for growth and development of plants.
4. Irrigation: Supplying water to plants at regular intervals.
5. Protection from Weeds: Removal of unwanted plants from the cultivated field to allow crops proper access to lights, space, and nutrients.
6. Harvesting: Cutting mature crops from fields.
7. Storage: Keeping grains or produce safe from rats, insects, microorganisms and moisture.
1. Preparation of soil: - Various processes are included in it-
(a) Ploughing
(b) Levelling
(c) Manuring
Ploughing: - The process of loosening and turning up the soil using a tool is called Ploughing or tilling.

Advantage of loosening of the soil-
Que: -Why is the soil turned and loosed before sowing seeds?
Why the farmer does turn the soil?
Why the preparation of soil is is an important step in growing a crop?
Ans: The soil is turn and loose before sowing seeds due to following reason-
1. It allows the roots to breath easily.
2. It helps the roots to penetrate deeper into the soil.
3. It allows mixing of manure and fertilizers more uniformly with the soil.
4. It allows the organisms such as earthworms, millipedes, bacteria and fungi to come up top and decompose the dead animals and plants.It increases the fertilities of soil.
5. It increases the water holding capacity of soil.


Ox-drawn Scraper Laser Land Leveller
Advantage of levelling of the soil-
Que: - Why is the soil levelled before sowing seeds?
Ans: The soil is levelled before sowing seeds due to following reason-
1. It breaks or crushes bigger chunks of dry soil into smaller pieces.
2. It protects the upper layer of soil from erosion by wind or water.
3. It prevents water logging and promote uniform irrigation.
Manuring: - The process of mixing manures with soil is called manuring.
ADVANTAGE OF MANURE:-
1. It increase the number of friendly microbes.
2. It increase soil fertility, water holding capacity, and aeration.
3. It reduce soil erosion.
4. It is cheap.
5. It provide humus.
DISADVANTAGE OF MANURE:-
1. They have less amount of nutrients as compared to fertilizers.
2. Manures are bulky and not easy to store and transport.
Que: Why are the earthworms known as farmer’s friends?
Ans:- Earthworms called as farmer’s friends because the burrowing action of earthworm helps to loosen the soil particles and improves the physical structure of soil by adding humus.
Agricultural Implements: -Those tools that are used in preparation of soil are called agricultural implements.
Ex: - Plough, Hoe, Seed-drill, Khurpa, Cultivator etc.

Plough: - The farming implement with one or more blades fixed in a frame, used to turn over the soil is called plough.
* The main part of Plough is a long log of wood called ploughshaft. One end of the shaft is handle and other end is attach to a beam which is placed on the bulls necks.
Ploughshare: -The main cutting blade of a plough.
Hoe: - A tool which is used for removing weeds and for loosening the soil is called hoe.
Cultivator: - The plough that is driven by a tractor is called cultivator.
* Cultivators are used instead of ploughs since they are faster.
* The use of cultivator saves labour and time.
|
|
Seed-drill: - The farming implement that is used for sowing the seeds uniformly at proper distance and depth is called seed-drill.
Trowel (Khurpa): - The farming implement that is used for loosening the soil and removing the weeds is called trowel.
2. Selection and Sowing of seeds: - After preparation of soil, seeds are selected. While selecting the seeds following suggestions should be kept in mind.
* Select only good quality, healthy, disease-resistant and high-yield seeds.
* Treat the seeds with fungicide before sowing.
Sowing:- The process of putting the seeds in the soil is known as sowing.
Methods of Sowing of seeds- Broadcasting Seed-drills
Broadcasting: - The process of scattering of seeds over the soil surface by hand is called broadcasting.
Seed-drills: - The process of scattering of seeds by seed-drill is called seed-drilling. In this process seeds are placed in the seed-bowl. As the plough moves, it makes furrows in the soil and the seeds are sown uniformly at proper distance and depth.

Transplantation: - The process in which seeds are sown first in nurseries, and then the seedlings are transferred into the main field is called transplantation.
Ex- Paddy, tomato, onion, chilli etc.
Advantages of transplantation: -
* It helps in selective cultivation of healthy seedlings. This results in better crop production.
* Transplantation permits better crop production.
* Transplantation permits better root penetration into the soil.
* Transplantation allows better shoot development.
Question: What is the traditional tool of sowing?
Answer: The traditional tool shape is like a funnel. The seeds are filled into the funnel which passes down through pipes having sharp ends. These sharp ends pierce into the soil and put seeds there.
Que: Give two reasons why seeds should be sown at correct distance?
Ans: Seeds should be sown at correct distance to avoid overcrowding.
i. If the seeds are too close the will not get enough water, sunlight, and nutrients.
ii. If the seeds are too far apart, there is wastage of field space.
3.Manures and Fertilizers: -
Manures: - Those organic substances that are obtained by the microbial decomposition of plants and animals waste are called manure.
Que: Why do we add manures and fertilizers in the soil?
Ans: Continuous growing of crop in the field causes deficiency of mineral nutrients in the soil. So, the manure is added to the soil to make up the deficiency of mineral nutrients.
Types of Manures
Farm yard: -It consists of cattle dung and urine.
Compost: - It is formed by the decomposition of plants and animals. If decomposition can be done in the presence of earth worm, it is known as vermicompost.
If decomposition is done in the presence of bacteria, then it is known as bacterial compost.
Green manure: - It consists of decomposed leguminous plants like sun hemp. Leguminous plants are the plants whose roots have special bacteria and that bacteria is helpful in nitrogen fixation.
Advantages of Manure
The advantages of manure are as follows –
1. It adds nutrient to soil.
2. It adds humus to soil.
3. It improves the quality of soil.
Disadvantages of Manure
* They have less amount of nutrients as compare to fertilizers.
* Manures are bulky and not easy to store and transport.
Fertilizers: -Those inorganic compounds which supply specific nutrients in the soil are called fertilizers.
Ex: - NPK (Nitrogen Phosphorous Potassium), ammonium sulphate, ammonium phosphate etc.
Types of fertilizers
Nitrogenous: Sodium nitrate, Urea
Phosphatic : Ammonium phosphate
Potassium : Potassium sulphate
Mixed : NPK,CAN (Calcium Ammonium nitrate)
Advantages of Fertilizers
* They are nutrient specific and required in small amounts.
* They are water soluble and absorbed by the plant easily.
* They are easy to store and transport.
Addition of manure and fertilizers: -Plants require nutrients for growth. They get these nutrients from the soil. This can be done either by natural methods or by adding manures and fertilizers to the soil.
Natural methods:
Field fallow: -The method of leaving the field without cultivating any crops to replenish nutrients in the soil.
Crop rotation:- It involves growing two or more crops alternatively on the same land in the same growing season so that the soil is not depleted of any particular nutrients.
4. Irrigation: - The watering of crops at different intervals is called irrigation. The time and frequency of irrigation vary from crop to crop, soil to soil and season to season. For examples-
* The frequency of irrigation in the summer is higher due to the increased rate of evaporation of water from soil and leaves.
* Sandy soil needs more water than clayey soil.
* Different crops need different amount of water at different stages of growth like at the flowering and at the grain-development stage.
* Wheat, Gram and Cotton crops need irrigation at regular intervals, but not the standing water.
* Paddy is transplanted in standing water and needs continuous irrigation.
Sources of irrigation: - The source by which we gate water for irrigation is called source of irrigation.
Ex- Pond, lake, river, Wells, tube wells, Dams, Canals etc.
 |
 |
| Well | Tubewell |
 |
 |
| Pond | Lakes |
 |
 |
| River | Dams |
 |
|
| Canels | |
Method of Irrigation: -
1. Traditional method of Irrigation
2. Modern methods of irrigation
1. Traditional method of Irrigation
The traditional methods of irrigation are as follows-
Moat: - Water is pulled out from the well and directly supplied to the plants.
Dhekli: - In dhekli, buckets are used and then with the help of rope, water is pulled out from the well.
Rahat: -In this method, buckets are knotted with rope on wheel and then bulls rotate the handle due to which wheel turned up and then water gets filled into the bucket and used for different purposes.
Chain pump: - In this method, two wheels are used. The one wheel is easily visible and the another wheel at the bottom is slightly dipped into the soil. These two wheels are connected with each other through chain and buckets are joined with wheel. When wheels rotate buckets get filled and used for different purposes.
 |
 |
| Moat(Pully system) | Chain Pump |
 |
 |
| Dhekli | Rahat (Lever system) |
2. Modern methods of irrigation
In modern methods, two methods are used which are as follows:
Sprinkler System
Drip system
Sprinkler: - In this method, water is distributed through a network of perpendicular pipes having rotating nozzles on their tops are linked to a main pipe. When water is pumped into the main pipe, it comes out of the rotating nozzles with pressure in all the directions.
* This system provides efficient coverage for small to large areas and is suitable for use on all types of soil.
* This method of supplying water is similar to rainfall.
* This system of irrigation is more useful for uneven dry lands.

Sprinkler
Drip system: -In this system, waterfalls drop by drop just at the position of roots. Drip Irrigation also called trickle irrigation.
* A drip irrigation system carries water directly to the base of each individual plant.
* Water is allowed to fall drop by drop from a pipe, just near the roots.
* It is an ideal watering method. It saves water. It also reduces soil erosion.
* Water and nutrients reach directly to the places where needed.
* It saves time and labour.
* This methods is used for fruit and flower plants.
Uses
* It is helpful in translocation of food.
* It protects the crops from frost and hot climate.

Drip system
Excess irrigation or water-logging: -When water accumulates around the plant by providing much water is called water-logging.
Disadvantages of excess irrigation
* Excess water and wet soil do not permit proper aeration of the seed/root of the plants.
* Water logging increases the amount of salt in the soil and damages the soil fertility.
* Due to excess irrigation seeds can’t respire.
* Due to excess irrigation roots do not grow well.
From Weeds and Weeding: -
Weeds: -Those unwanted plants that grow along with the main plant are called weeds.
Ex- Amaranthus (chaulai), grass, wild oats(javi), Chenopodium(bathua) etc.
Weeding: - The process of removing weeds is called weeding.
Disadvantages of weeds: -Weeds grow with main crops and take nutrients, space, sunlight, water etc. Due to weeds, main crop gets affected.
Methods of weeding
Manual weeding: It is the method in which weeding is done by hands. This process is time consuming.
* Weedicides: These are the chemicals that are used to kill weeds.
Ex: 2-4 D, MCPA, Butachlor etc. In these methods we spray the chemicals.
Protection of crops: - Crops are protected from pests.
Pests are the organisms that damage crops. For example: Insects, bacteria etc.
Pests affect crops in various ways as follows-
1. They lower the quality of crops.
2. They reduce yield.
3. They bore inside the crops.
Pests are removed by pesticides. Pesticides are the chemicals that kill pests. For example: DDT.BHC and Malathion etc.
Harvesting: - The process of cutting and gathering mature crops from the field with sickle is called harvesting.

Methods of Harvesting: -
Threshing
Winnowing
Threshing: - The process of separating grain from hay and chaff is called threshing.

Winnowing: - The process of separating chaff from grains is called winnowing.

Combine harvester: - The farm machine which does both harvesting as well as threshing is called Combine harvester.
Storage: - If storage is not done in well maintained order, our crops get destroyed.
Dry storage: -There are certain seeds that need dry storage.
Ex- Food grain etc.
Cold storage: -There are certain seeds that need cold temperature for its storage.
Ex- Fruits including apples, banana, pear etc.
Methods Employed for storage
Drying: -Seeds can be stored by drying as by doing this, moisture gets removed and it prevents the growth of microorganisms.
Maintaining storage containers: - Gunny bags, earthen pots, etc should not be used repeatedly. It should always be new, without cracks etc. By doing this, microorganisms will not grow and seeds can be saved for a longer period of time.
Chemical treatment: - Godowns, etc. should be sprayed with fumigants and there should be no seepage so that crops can be stored properly. If water is present in godowns, it may lead to formation of microorganisms and these microorganisms might spread diseases. Thus, it can harm storage.
Uses of improved storage structures: -The storage structures that are airtight, rat proof, can maintain steady temperature etc should be used. For example: silos.
Advantages of storage
* Food does not get spoiled.
* It protects them from pests like rodents, microbes or insects.
* It is helpful in availability of fruits & vegetable whole year.
* It is also helpful in maintenance of emergency stock like during flood.
Granaries or silos: -The tall tower that is used to storage of grains on large scale is granaries or silos.
Increasing crop produce: - Crop produce can be increased by increasing the land under cultivation, by improvement in the methods of agriculture, and by developing better varieties of crops by plant breeding.
Hybridization:- The process of plant breeding in which new varieties with desired characteristics of high yield and resistance to disease, are developed is called hybridization.
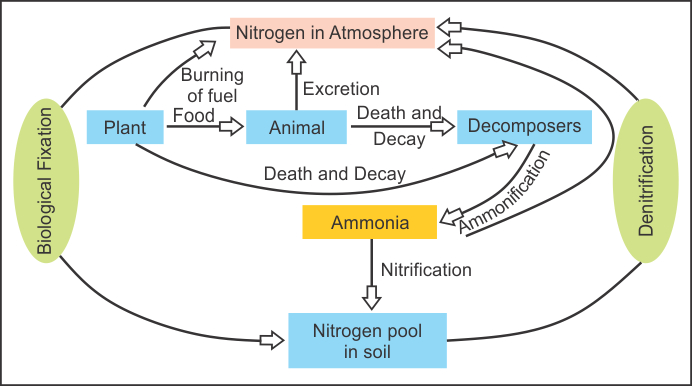
Nitrogen cycle: - The cyclic process of nitrogen being fixed, used by plants and animals and later returned to the atmosphere is called nitrogen cycle.
* Air contains about 78% nitrogen.
* Nitrogen is used by life forms for the formation of protein, amino acids and nucleic acids.
* This transformation can be carried out through both biological and physical processes.
Nitrogen cycle involves the following steps:
Nitrogen fixation: -The fixing of atmospheric nitrogen into nitrate (inorganic compounds) by Rhizobium is called nitrogen fixation.
Nitrate Assimilation: - Converting nitrate into usable (proteins) organic compounds in organisms is called nitrate assimilation.
* Plants absorb nitrates from the soil through their root system and convert them into plant proteins. When animals eat these plants, the plant proteins are converted into animal proteins.
Ammonification: -The process of conversion of plant and animal proteins into ammonium compounds by putrefying bacteria in soil is called ammonification.
Nitrification: -The ammonium salts are converted into nitrites by Nitrosomonas bacteria. The nitrites are then converted into nitrates by Nitro bacteria. This process is called nitrification.
Denitrification: - The conversion of nitrates into free nitrogen gas by denitrifying bacteria (seudomonas bacteria) is called denitrification.
Animal husbandry: - The part of agriculture in which we study about breeding, feeding and caring of domestic animals for food and other purposes is called animal husbandry.
* Animal husbandry has been practiced for thousands of years since the first domestication of animals (dog). Humans are dependent on animals in innumerable ways. The animals are domesticated by humans for many purposes. Depending on the usefulness of domestic animals they are categorized as:
Different categories of animals
Milch Animals: Those animals which give milk are called milch animals.
Ex:- Cow, buffalo, and goat.
Meat and egg giving animals:
Those animals which give egg and meat are called meat and egg yielding animals.
Ex- Pig, cattle, and hen.
Draught animals (Working animals)
Those animals which are used for working purpose are called draught animals.
Ex- Buffalo, Camel, Horse, Donkey etc.
Needs of Animal Husbandry
As animals are serving various purposes, so there is a need to take care of them. This will help us improve livestock and extract maximum use from them. Moreover, their dung, urine, etc is also used as manure (used to maintain fertility of soil).
Note-
* Rearing of fish for food on large scale is called pisciculture.
* Rearing of honeybee on large scale is called apiculture.